How is the embodied energy of objects calculated?
Suasì adopts the Cumulative Energy Demand (CED) system for products.
It is a metric used to quantify the total amount of energy required throughout the entire life cycle of a product or service. This includes all forms of energy consumed during the production, use, and disposal phases.
CED can be broken down into various types of energy, such as renewable and non-renewable energy, and provides a comprehensive overview of a product’s energy impact. It is derived from the application of LCA analysis models to industrial production.
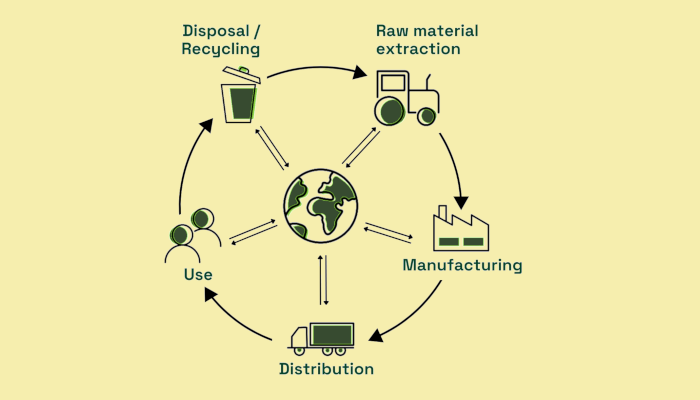
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a methodology used to evaluate the overall environmental impact of a product or service throughout its life cycle. LCA considers every stage of the product’s life cycle, including:
- Raw material extraction and processing: energy and resources required to extract and prepare raw materials.
- Production and manufacturing: Energy used in factories to transform raw materials into finished products.
- Distribution and transportation: Energy required to transport products from production sites to places of use.
- Use and maintenance: Energy consumed during the product’s use phase, including energy for maintenance and repair.
- End-of-life and disposal: Energy required for recycling, reuse, or waste management of the product at the end of its life.